Mini-split HVAC systems provide quiet, energy-efficient heating and cooling with flexible, room-by-room comfort all year.
CERTIFIED HVAC TECHNICIANS FOR QUALITY HOME VENTILATION Heating Replacement
Services & Repairs
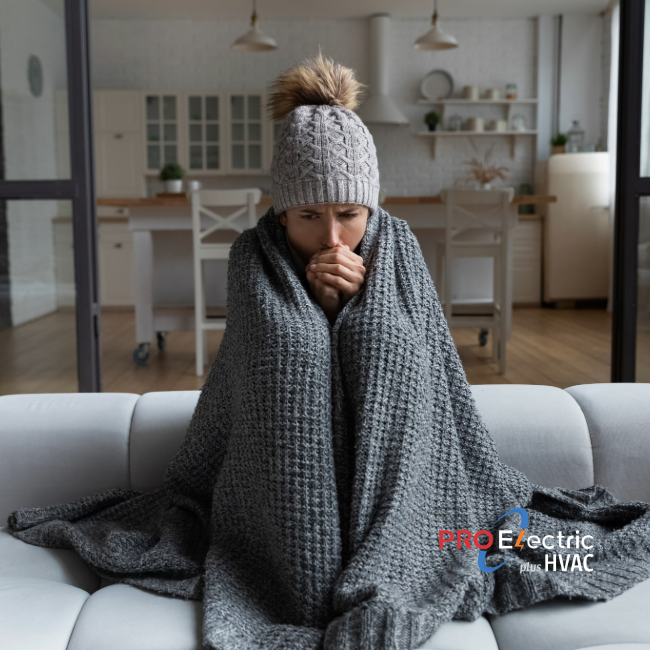
Keeping Homeowners Warm with our Expert Heating Services in Fairfax, Loudoun, Arlington, and Prince William Counties.
BY PETER | HVAC TECHNICIANLatest Heating System Insights
TOP 50 QUESTIONS & ANSWERSHeating FAQS
50 HEATING SYSTEM FAQs
Q1: Why is my furnace or heater not turning on at all?
A: Older gas furnaces often fail to start when the pilot light has gone out. If the pilot is not lit, the burner cannot ignite. If it repeatedly goes out, the system needs professional service.
Q2: What if my newer furnace does not have a pilot light but still will not turn on?
A: Newer furnaces use an electric igniter instead of a pilot flame. If the igniter fails or burns out, the furnace cannot light and will not heat.
Q3: Could the problem be related to the flame sensor?
A: Yes. A dirty or failing flame sensor can incorrectly signal that no flame is present, causing the furnace to shut down for safety.
Q4: Why do I sometimes smell gas when the furnace runs?
A: This can result from dirty burners. Soot and debris buildup can cause inefficient combustion and reduced heat output. Burner cleaning is part of routine maintenance.
Q5: Can the burner become clogged?
A: Yes. Burners can become blocked by debris, rust, or insect activity. A clogged burner restricts gas flow and prevents proper ignition.
Q6: What controls the gas flow into the burner?
A: The gas valve regulates gas flow. If it fails mechanically or electrically, the burner may not receive the correct amount of fuel.
Q7: I have an oil furnace. Can the oil valve fail?
A: Yes. Oil furnaces use an oil control valve. If it malfunctions, the burner may not receive the correct fuel supply.
Q8: Can low gas pressure prevent my furnace from working?
A: Yes. If incoming gas pressure is too low, the furnace will not receive enough fuel to operate correctly. Your gas company may need to inspect the supply.
Q9: Can oil furnaces experience low oil pressure?
A: Yes. Low oil pressure can result from a failing oil pump, a clogged filter, or fuel line issues.
Q10: Can a blocked fuel line stop my furnace?
A: Yes. Blocked gas or oil lines prevent fuel from reaching the burner, resulting in no heat.
Q11: Is a cracked heat exchanger dangerous?
A: Yes. A cracked heat exchanger can allow combustion gases, including carbon monoxide, to enter the home. If suspected, shut off the furnace and seek immediate service.
Q12: Can heat exchangers corrode over time?
A: Yes. Rust and corrosion weaken the metal and increase the risk of cracking or failure.
Q13: What does a heat exchanger leak mean?
A: A leak typically refers to combustion gases escaping through openings in the exchanger, which is a serious safety concern.
Q14: Does the blower motor affect heating?
A: Yes. The blower motor circulates heated air throughout the home. If it fails, the furnace may produce heat but not distribute it.
Q15: Can a faulty blower motor capacitor affect heating?
A: Yes. A capacitor helps the blower motor start and run. If it fails, the blower may not operate.
Q16: Can a dirty blower fan affect heating?
A: Yes. Dust buildup on the blower fan reduces airflow, lowers efficiency, and strains the furnace.
Q17: Can furnace vents become blocked and affect heating?
A: Yes. Snow, ice, leaves, or debris blocking the vent can prevent safe exhaust and force the furnace to shut down.
Q18: What is vent backdraft?
A: Vent backdraft occurs when combustion gases flow back into the home instead of being vented outside. It is a serious safety issue.
Q19: Can vent pipes corrode?
A: Yes. Moisture can corrode vent pipes over time, weakening them and reducing safe airflow.
Q20: Can a faulty thermostat stop the furnace from turning on?
A: Yes. If the thermostat is malfunctioning, it may not signal the furnace to operate.
Q21: What if my thermostat is not broken but still not heating correctly?
A: The thermostat may be miscalibrated and inaccurately reading the temperature, causing improper heating cycles.
Q22: What is limit switch failure?
A: The limit switch prevents overheating by shutting down the furnace if temperatures get too high. If it fails, overheating risks increase.
Q23: What does the rollout switch do?
A: The rollout switch shuts the furnace down if flames move outside the burner area, which is a hazardous condition.
Q24: What happens if the furnace control board fails?
A: The control board manages all furnace components. Failure can prevent ignition, airflow, or safe operation.
Q25: Do furnaces use relays and can they fail?
A: Yes. Relays act as electrical switches and can prevent components like fans or igniters from working when they fail.
Q26: Can wiring corrosion affect heating systems?
A: Yes. Corroded wiring causes poor electrical connections, shorts, and intermittent heating failures.
Q27: Do loose wiring connections affect furnace operation?
A: Yes. Loose or failing connections can cause intermittent heating or system shutdowns.
Q28: What does a transformer do in a furnace?
A: It reduces household voltage to the lower voltage needed for control circuits. If it fails, the furnace cannot operate.
Q29: Do I still need to change my air filter during heating season?
A: Yes. A clogged filter restricts airflow, reduces efficiency, and can cause overheating.
Q30: Can duct leaks affect heating?
A: Yes. Leaky ducts allow heated air to escape, increasing energy use and reducing comfort.
Q31: Can ducts become blocked and affect heating?
A: Yes. Blocked ducts restrict airflow and prevent heat from reaching certain rooms.
Q32: What is zone valve failure?
A: In zoned systems, zone valves control heating distribution. If a valve fails, a zone may lose heat or overheat.
Q33: What is circulator pump failure?
A: In boiler systems, the circulator pump moves hot water through pipes and radiators. If it fails, heat cannot distribute.
Q34: Can circulator pumps have capacitor failures?
A: Yes. A failing capacitor can prevent the pump from starting or running correctly.
Q35: Is low boiler water level dangerous?
A: Yes. Low water can cause overheating, system damage, and in extreme cases, boiler failure. Immediate service is required.
Q36: Why would a boiler pressure relief valve leak?
A: A leaking relief valve indicates excessive system pressure or a failing valve that needs inspection.
Q37: What is boiler expansion tank failure?
A: The expansion tank absorbs pressure changes. If it fails, system pressure may rise and cause leaks or valve activation.
Q38: What is boiler scale buildup?
A: Scale is mineral accumulation inside a boiler. It reduces efficiency and can cause overheating.
Q39: Can boilers develop internal corrosion?
A: Yes. Rust inside the boiler weakens the tank, causes leaks, and reduces system lifespan.
Q40: What is electric heating element burnout?
A: Electric heaters use elements similar to coils. If an element fails, heating output decreases or stops.
Q41: Can wiring faults affect electric heaters?
A: Yes. Wiring problems can cause heater failure, breaker trips, or fire hazards.
Q42: Can electric heater thermostats fail?
A: Yes. Built in thermostats on electric heaters can malfunction, preventing correct operation.
Q43: Can a heat pump compressor fail in heating mode?
A: Yes. The compressor operates in both heating and cooling. Failure results in no heat.
Q44: What happens if the heat pump reversing valve fails?
A: A failing reversing valve may prevent the system from switching to heating mode.
Q45: What is heat pump defrost malfunction?
A: In winter, frost accumulates on the outdoor coil. If the defrost cycle fails, the heat pump loses heating capacity.
Q46: Why does the outdoor fan motor matter in winter?
A: The fan must pull air across the outdoor coil to extract heat. If it fails, heating performance drops.
Q47: Can refrigerant leaks affect heating?
A: Yes. Low refrigerant reduces the system’s ability to transfer heat.
Q48: What happens if the heat pump has low refrigerant charge?
A: Low charge leads to weak heating performance and poor efficiency.
Q49: Does system age affect heating reliability?
A: Yes. Older components wear out and become less efficient, leading to more frequent breakdowns.
Q50: Does heating equipment need maintenance?
A: Yes. Regular maintenance improves safety, efficiency, and reliability while preventing major issues throughout the heating season.
WE TAKE PRIDE IN WHAT WE DO!Customer Reviews
FAIRFAX, ARLINGTON, LOUDOUN, & PRINCE WILLIAM COUNTIESGet a Free Heating Estimate
Our experienced technicians quickly fix your heater to ensure your home remains comfortable. Contact us today for reliable and affordable service.
Recent Jobs and Reviews in Falls Church, VA
FAIRFAX, ARLINGTON, LOUDOUN, & PRINCE WILLIAM COUNTIESHVAC Service Areas
Northern Virginia